Industrial Valve Technologies and Flow Control Equipment
Industrial valve technologies enable precise control of liquids, gases, and other media across numerous applications. By understanding the functions and configurations of these systems, businesses can see how flow control contributes to safe, efficient, and predictable industrial operations.
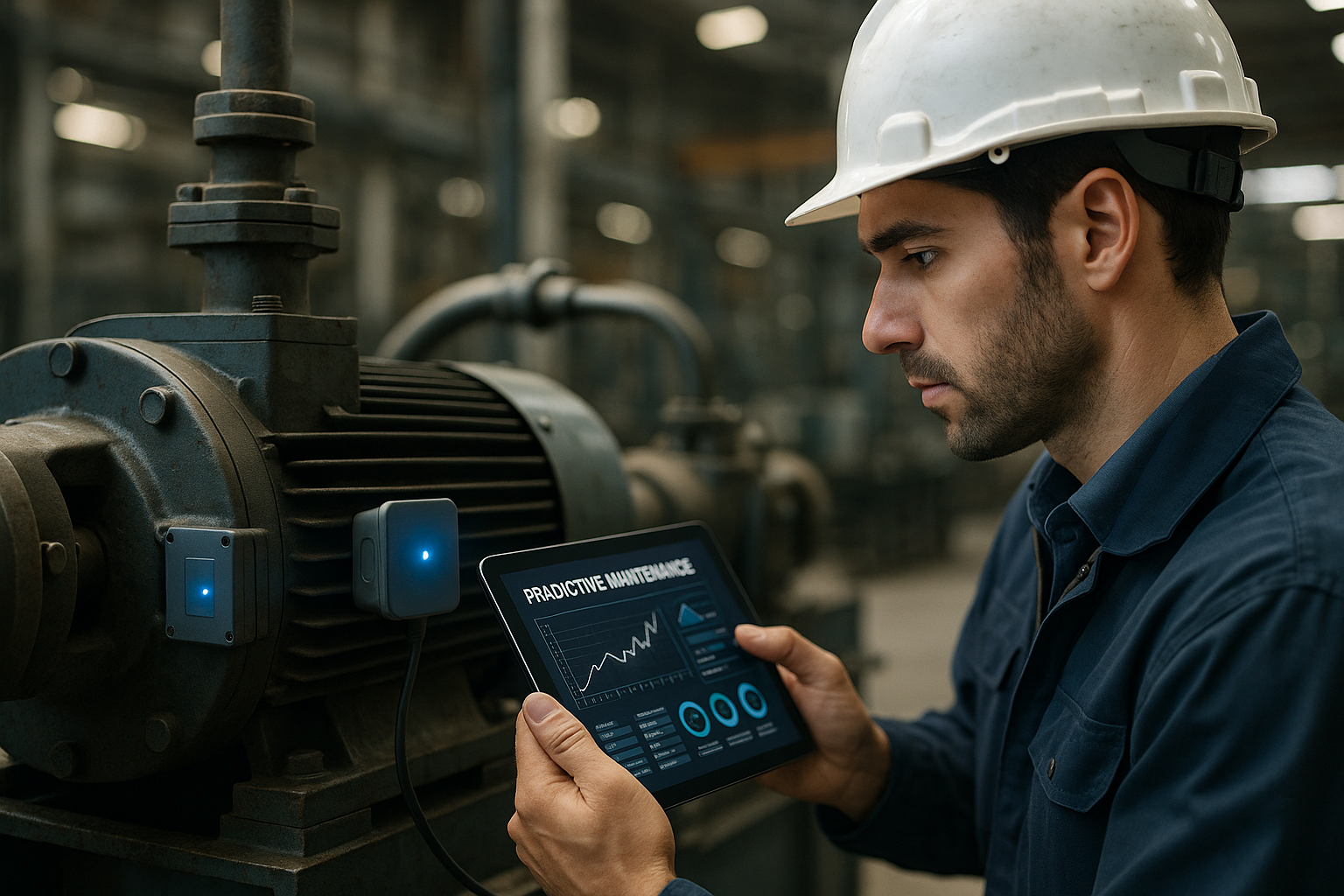

Types of Industrial Valves and Flow Control Devices
Industrial valve systems encompass numerous designs, each engineered for specific operational requirements. Gate valves provide reliable shut-off capabilities in pipeline systems, while globe valves offer precise flow regulation through their linear motion design. Ball valves deliver quick quarter-turn operation with excellent sealing properties, making them ideal for frequent operation cycles.
Butterfly valves present cost-effective solutions for large-diameter applications, utilizing a rotating disc mechanism that minimizes pressure drop. Check valves prevent backflow automatically, protecting equipment and maintaining system integrity. Pressure relief valves serve as critical safety devices, releasing excess pressure to prevent catastrophic failures.
Specialty valves include diaphragm valves for corrosive media handling, pinch valves for slurry applications, and control valves with actuators for automated process control. Each valve type addresses specific challenges related to pressure ratings, temperature ranges, fluid compatibility, and operational frequency.
How Flow Control Equipment Supports System Reliability
Flow control equipment enhances system reliability through multiple mechanisms that maintain operational stability and prevent equipment failures. Proper flow regulation prevents cavitation, water hammer, and excessive pressure fluctuations that can damage downstream components. Control valves with feedback systems automatically adjust to maintain setpoint conditions, reducing operator intervention and human error risks.
Redundant valve configurations provide backup protection when primary components fail. Emergency shutdown valves respond rapidly to safety signals, isolating hazardous sections within seconds. Flow measurement devices integrated with control systems enable predictive maintenance by monitoring performance trends and detecting anomalies before failures occur.
Advanced flow control systems incorporate smart diagnostics that continuously monitor valve position, actuator performance, and seal integrity. These systems generate maintenance alerts, optimize replacement schedules, and provide detailed operational data for reliability analysis.
Considerations When Selecting Valve Technologies
Selecting appropriate valve technologies requires comprehensive evaluation of operational parameters and system requirements. Pressure and temperature ratings must exceed maximum operating conditions with adequate safety margins. Fluid characteristics, including corrosivity, abrasiveness, and viscosity, determine suitable materials and sealing technologies.
Flow capacity calculations ensure valves can handle required throughput without excessive pressure drops. Installation space constraints influence valve configurations, with compact designs preferred in crowded equipment areas. Maintenance accessibility affects long-term operational costs, favoring designs with replaceable components and straightforward service procedures.
Actuation requirements depend on automation levels, response times, and fail-safe positions. Manual valves suit infrequent operations, while automated systems require electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators. Environmental factors such as ambient temperature, vibration, and explosion hazards impact housing materials and certification requirements.
| Valve Type | Applications | Key Features | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gate Valve | Pipeline isolation | Full bore, minimal pressure drop | $200 - $5,000 |
| Ball Valve | General service | Quarter-turn, tight shutoff | $150 - $3,500 |
| Globe Valve | Flow regulation | Precise control, good throttling | $300 - $4,000 |
| Butterfly Valve | Large diameter lines | Lightweight, space-saving | $400 - $8,000 |
| Control Valve | Process automation | Modulating control, actuated | $1,500 - $25,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Trends in Industrial Valve Design
Contemporary valve design trends emphasize digitalization, sustainability, and enhanced performance capabilities. Smart valve technologies integrate sensors, wireless communication, and diagnostic capabilities that provide real-time performance data to control systems. These developments enable predictive maintenance strategies and optimize operational efficiency.
Environmental considerations drive development of low-emission valve designs with improved sealing technologies and fugitive emission controls. Advanced materials, including ceramic coatings and specialized alloys, extend service life in harsh operating conditions while reducing maintenance requirements.
Modular valve designs facilitate component replacement and system upgrades without complete valve replacement. Standardized interfaces and communication protocols improve interoperability between different manufacturers’ equipment, reducing integration complexity and costs.
Additive manufacturing technologies enable custom valve components with complex internal geometries that optimize flow patterns and reduce turbulence. These innovations particularly benefit specialized applications requiring unique performance characteristics not achievable through conventional manufacturing methods.
Modern valve technologies continue evolving to meet increasing demands for efficiency, reliability, and environmental compliance. Understanding these developments helps industrial operators make informed decisions about equipment selection and system design. Proper valve selection and maintenance practices ensure optimal performance throughout equipment lifecycles, supporting operational goals while maintaining safety standards and regulatory compliance.